Are your heating bills sky-high, despite cranking up the thermostat? Do you feel drafts even with the windows closed? Your home might be leaking money – and comfort – through inadequate or, worse, incorrectly installed insulation. Getting home insulation wrong isn't just an inconvenience; it’s a costly mistake that can lead to dampness, mold, structural damage, and health problems. This ultimate guide reveals the science behind perfect home insulation, empowering you to make informed decisions and avoid common pitfalls.
Why is Home Insulation So Important? (The Cold, Hard Facts)
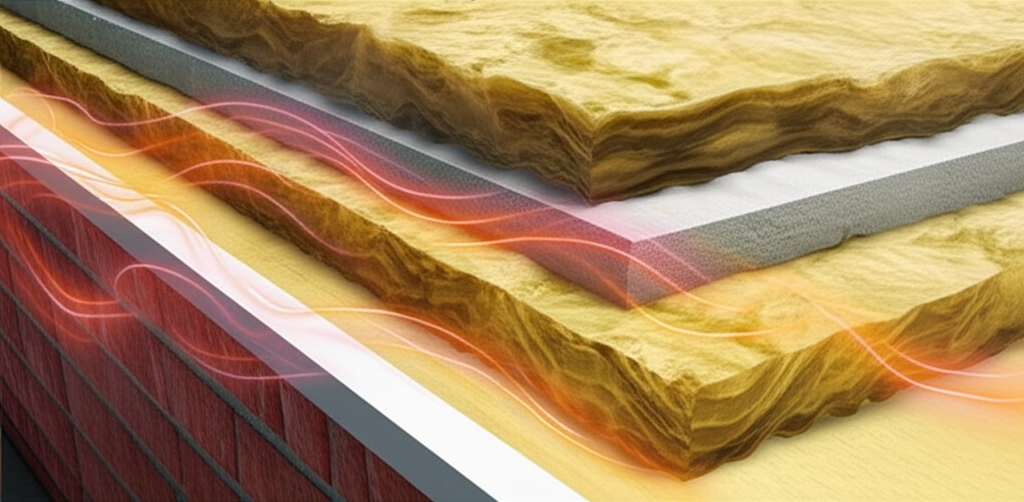
Imagine your house as a thermos. Its job is to keep the inside temperature stable, regardless of what's happening outside. Proper insulation is the key component of that thermos, preventing heat from escaping in the winter and keeping it out in the summer. Without it, you're essentially throwing money out the window (literally!).
- Massive Heat Loss: Research shows that up to 33% of your home's heat can escape through uninsulated walls. [1] That's a third of your heating bill vanishing into thin air!
- Increased Energy Bills: Poor insulation forces your heating and cooling systems to work harder, leading to higher energy consumption and increased costs.
- Reduced Comfort: Drafts, cold spots, and inconsistent temperatures make your home uncomfortable to live in.
- Environmental Impact: Higher energy consumption contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change.
How Does Home Insulation Work? (The Science Explained)
Insulation works by reducing heat transfer through conduction, convection, and radiation.
- Conduction: Heat transfer through direct contact. Insulation materials, like fiberglass or foam, have low thermal conductivity, meaning they resist the flow of heat.
- Convection: Heat transfer through the movement of fluids (air or water). Insulation prevents air movement within walls and ceilings, reducing convective heat loss.
- Radiation: Heat transfer through electromagnetic waves. Some insulation materials have reflective surfaces that can reduce radiant heat gain in the summer.
What Are the Different Types of Home Insulation? (Choosing the Right Fit)
Choosing the right type of insulation depends on several factors, including your climate, budget, and the specific area of your home you're insulating. Here's a breakdown of common options:
- Fiberglass: The most widely used and affordable option. Available in batts, rolls, and loose-fill.
- Pros: Cost-effective, readily available.
- Cons: Can lose effectiveness if it gets wet, requires proper installation to avoid gaps.
- Cellulose: Made from recycled paper. Typically blown into walls and attics.
- Pros: Environmentally friendly, good at filling small spaces.
- Cons: Can settle over time, may require professional installation.
- Spray Foam: Expands to fill gaps and create an airtight seal. Available in open-cell and closed-cell varieties.
- Pros: Excellent insulation value, air barrier, can add structural strength.
- Cons: More expensive than other options, requires professional installation.
- Mineral Wool (Rockwool/Slag Wool): Made from recycled glass, rock, or slag. Available in batts and loose-fill.
- Pros: Fire-resistant, good sound insulation, moisture-resistant.
- Cons: Can be more expensive than fiberglass.
- Rigid Foam Boards (EPS, XPS, Polyiso): Used for insulating walls, roofs, and foundations.
- Pros: High insulation value, water-resistant.
- Cons: Can be flammable, may require special installation techniques.
Where Should I Insulate My Home? (Prioritizing Key Areas)
Focus on these key areas to maximize your insulation efforts:
- Attic: A significant amount of heat is lost through the roof. Insulating your attic is one of the most cost-effective ways to improve energy efficiency.
- Walls: Insulating exterior walls can significantly reduce heat loss and gain. Consider both cavity wall insulation and external wall insulation (EWI).
- Floors: Insulating floors, especially over unheated spaces like crawl spaces or garages, can improve comfort and reduce energy bills.
- Basement: Insulating basement walls can prevent heat loss and reduce moisture problems.
What is External Wall Insulation (EWI)? (A Deep Dive)
External Wall Insulation (EWI) involves wrapping the exterior of your house in a layer of insulation, then covering it with a protective render. It's like giving your house a thermal overcoat.
Why Choose EWI?
- Improved Energy Efficiency: Significantly reduces heat loss and energy bills.
- Enhanced Comfort: Eliminates drafts and cold spots.
- Aesthetic Upgrade: Can improve the appearance of your home.
- Protection from the Elements: Protects the underlying structure from weather damage.
The EWI Nightmare: What Can Go Wrong?
While EWI offers many benefits, it's crucial to understand the potential pitfalls:
- Moisture Trapping: If not installed correctly, EWI can trap moisture inside the walls, leading to dampness, mold, and structural rot.
- Cracking: Cracks can appear in the render due to improper installation or movement of the building.
- Delamination: The render can separate from the insulation layer due to moisture or poor adhesion.
How to Avoid EWI Disasters: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Thorough Assessment: Conduct a detailed survey of your property to identify any existing problems, such as cracks, dampness, or structural issues.
- Hygrothermal Analysis: This crucial step assesses the moisture behavior of your walls and predicts the risk of condensation. It helps determine the appropriate type of insulation and ventilation system.
- Breathable Systems: For older homes, especially those with solid walls, choose a breathable EWI system that allows moisture to escape. Mineral wool is a good option.
- Proper Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation to remove moisture from the air. This may involve installing trickle vents in windows, extractor fans in bathrooms and kitchens, or mechanical ventilation systems.
- Qualified Installers: Hire experienced and accredited installers who are familiar with the specific EWI system you're using. Check their references and past work.
- Correct Installation Techniques: Pay attention to details like adhesive application, gap filling, mesh overlapping, and window/door detailing.
- Insurance-Backed Guarantee: Insist on an insurance-backed guarantee that covers defects in materials, design, and workmanship.
How Much Does Home Insulation Cost? (ROI Considerations)
The cost of home insulation varies depending on the type of insulation, the size of your home, and the complexity of the installation. While it can be a significant investment, the long-term energy savings and increased comfort can provide a good return on investment. Get multiple quotes from different contractors and compare their prices and services.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is R-value?
R-value measures an insulation material's resistance to heat flow. The higher the R-value, the better the insulation. The recommended R-value varies depending on your climate and the area of your home you're insulating.
How do I know if my home is properly insulated?
Signs of inadequate insulation include high energy bills, drafts, cold spots, condensation, and mold growth. A professional energy audit can help identify areas where your home is losing heat.
Can I install insulation myself?
Some types of insulation, like fiberglass batts, can be installed by homeowners. However, other types, like spray foam and EWI, require professional installation to ensure proper performance and avoid potential problems.
Conclusion: Invest in a Warmer, Healthier Home
Perfect home insulation is an investment in your comfort, health, and financial well-being. By understanding the science behind insulation, choosing the right materials, and hiring qualified professionals, you can avoid costly mistakes and create a home that's warm, energy-efficient, and comfortable for years to come. Don't let another winter pass with sky-high heating bills! Take action today and start insulating your home for a brighter, warmer future.
Ready to take the next step? Contact a local insulation contractor for a free consultation and energy audit!